Are you a Physical Therapist / Physiotherapist or Occupational Therapist working with people using wheelchairs? Check out these Startup Resources.
What is Dynamic Seating?
What is Dynamic Seating? A Definition
Our most-read blog is one that defines Dynamic Seating. That initial blog was posted about 4 years ago, so we wanted to revisit this foundational topic.
How do you know if Dynamic Seating is needed?
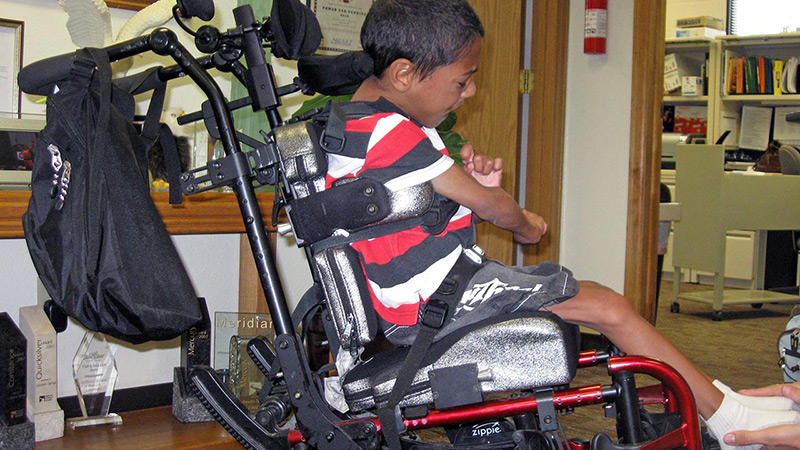
How Do I Know if a Client Needs Dynamic Seating?
In earlier blogs we have addressed key topics such as “What is Dynamic Seating” and “Dynamic Seating: Clinical Indicators.” In this blog series, we will take a look from the other side – what can you currently observe that indicates this person could benefit from Dynamic Seating?
Assessment
Evaluation, Simulation, and Dynamic Seating Trials
Recently a therapist asked me how she could recommend Dynamic Seating components if she didn’t actually try these with a client. Great question! It is not typically realistic to conduct Dynamic Seating trials as one would need to place Dynamic Seating components on a client’s wheelchair for trial and often the frame would need to be modified to accept these components.
RESNA Position Paper on Dynamic Seating
RESNA Position on the Application of Dynamic Seating
The purpose of this document is to share typical clinical applications as well as provide evidence from the literature supporting the application of dynamic seating to assist practitioners in decision-making and justification.